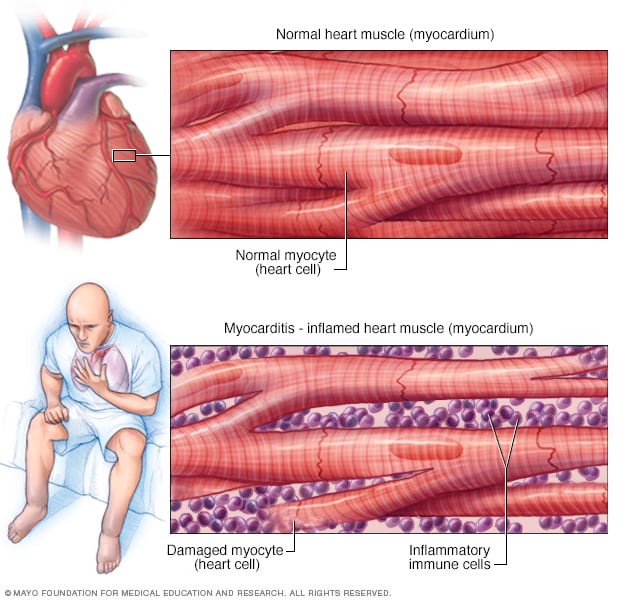
Myocarditis : Myocarditis
Difficulty breathing when resting. These muscles are very important to us because they ensure that our heart can supply our body with all the nutrition and oxygen that we need.

The Quest For New Approaches In Myocarditis And Inflammatory Cardiomyopathy Journal Of The American College Of Cardiology
All patients were males with a median age of 23 years.
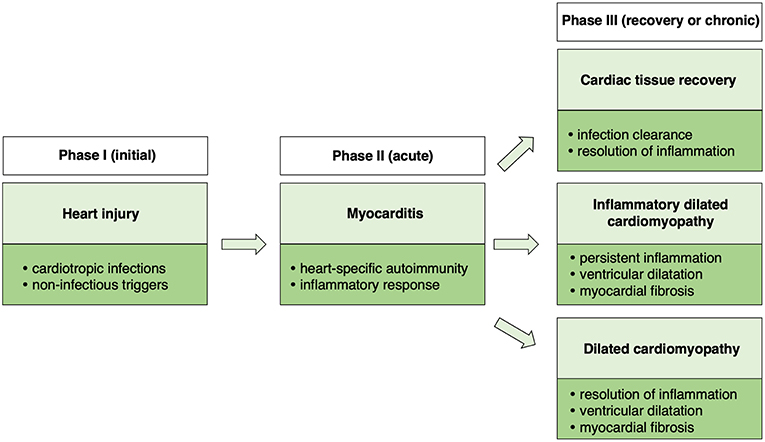
Myocarditis. Myocarditis may present with a wide range of symptoms ranging from mild dyspnea or chest pain that resolves without specific therapy to cardiogenic shock and death. Myocarditis can result from infection with Borrelia burgdorferi Lyme disease and patients with myocarditis due to Lyme disease are occasionally coinfected with ehrlichia or babesia. Myocarditis and cardiomyopathy are leading causes of heart transplants in the US.
Symptoms can include chest pain shortness of breath or palpitations. In very rare cases myocarditis can lead to sudden death. 16 Cases have also been reported after the influenza tetanus human papillomavirus and hepatitis B vaccines.
Common symptoms of myocarditis include. Symptoms of myocarditis include chest pain shortness of breath fatigue and fluid accumulation in the lungs. Shortness of breath when lightly exercising or walking.
A stabbing pain andor tightness in the chest which may spread across the body. In the reported COVID-19 cases with myocarditis in the literature clinical presentations have varied. The diagnosis of myocarditis was established after cardiac MRI.
Myocarditis is inflammation of the heart muscle and pericarditis is inflammation of the lining outside the heart. Clinicians who suspect myocarditis or pericarditis should consider consulting with a pediatric cardiologist infectious disease specialist andor rheumatologist. They should report cases of myocarditis andor pericarditis after COVID-19 vaccination to VAERS.
73 ECG changes suggestive of acute myocardial ischemia typically may include ST-segment elevation in 2 contiguous leads 54 T. Post-vaccination myocarditis has been reported most notably after the smallpox vaccine 15 with a prospective study suggesting a relative risk of clinical myopericarditis of greater than 200-times higher than published background rate. Flu-like symptoms such as a high temperature tiredness and fatigue.
Myocarditis is inflammation of the heart muscle and pericarditis is inflammation of the outer lining of the heart. In both cases the bodys immune system is causing inflammation in response to an infection or some other trigger. Myocarditis was diagnosed in all patients there was no evidence of COVID-19 infection.
It is a clinical syndrome of non-ischaemic myocardial inflammation resulting from a heterogeneous group of infectious immune and non-immune diseases. Myocarditis is clinically and pathologically defined as inflammation of the myocardium in the absence of the predominant acute or chronic ischaemia characteristic of coronary artery disease. Established myocarditis is a relatively rare sequelae of COVID-19 infection.
Five patients presented after the second and one after the first dose of the vaccine. 97172 Elevated troponin levels have proven to be a more reliable predictor of myocardial injury than levels of creatine kinase. The myocardium is the technical medical name for the hearts muscles.
Additional safety data presented Thursday looked at adverse events in adolescents ages. Treatment mainly involves preventing heart failure with medication and diet as well as monitoring for heart rhythm abnormalities. Myocarditis is a disease marked by the inflammation of the heart muscle known as the myocardium the muscular layer of the heart wall.
There is potential overlap in symptomatology in patients with primary COVID-19 infection and COVID-19 patients with clinically suspected myocarditis. Myocarditis is an inflammation of the heart muscle and can be caused by a variety of infections conditions and viruses. Dilated cardiomyopathy with chronic heart failure is the major long-term sequela of myocarditis.
In both cases the bodys immune system causes inflammation in response to an infection or some other trigger. Myocarditis masquerading as an acute coronary syndrome has also been well described.
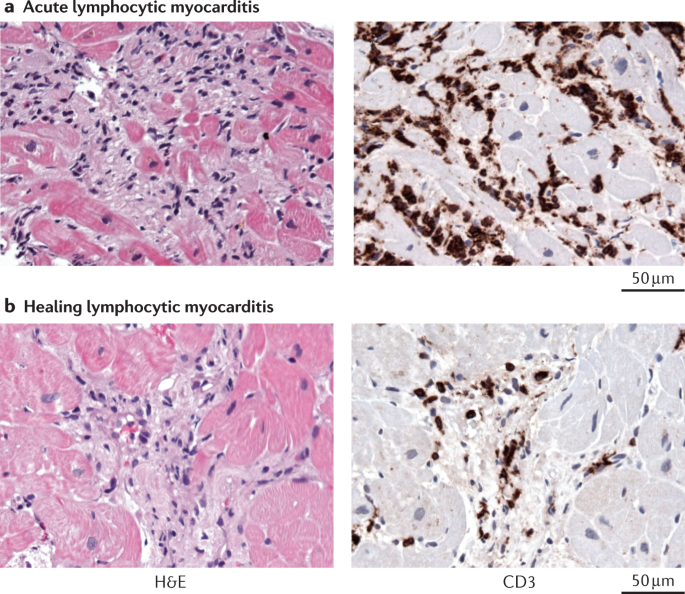
Myocarditis And Inflammatory Cardiomyopathy Current Evidence And Future Directions Nature Reviews Cardiology

Myocarditis In A 16 Year Old Boy Positive For Sars Cov 2 The Lancet
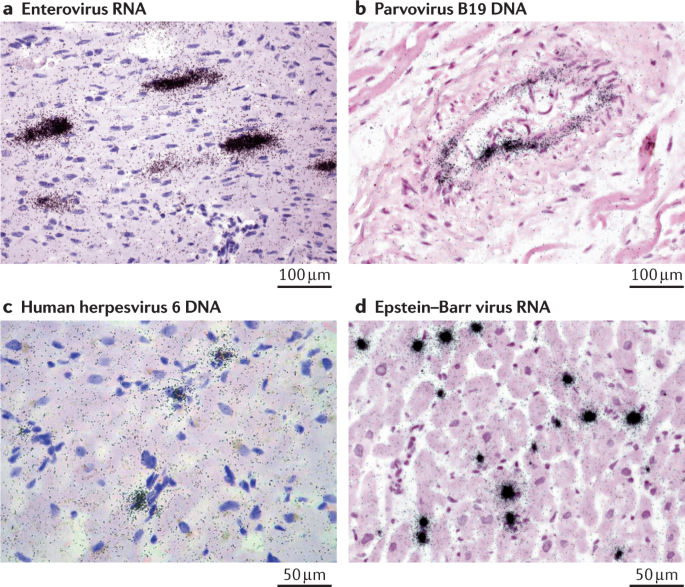
Myocarditis And Inflammatory Cardiomyopathy Current Evidence And Future Directions Nature Reviews Cardiology
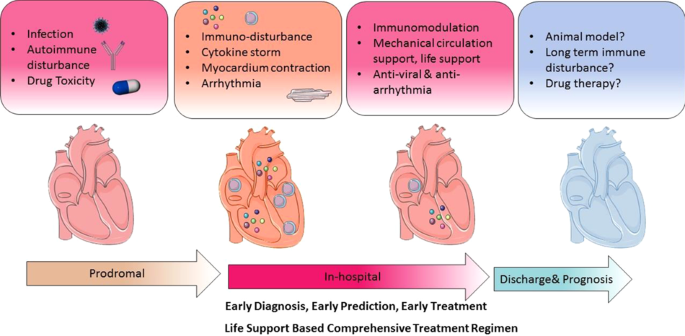
Fulminant Myocarditis A Comprehensive Review From Etiology To Treatments And Outcomes Signal Transduction And Targeted Therapy

Frontiers Myocarditis In Humans And In Experimental Animal Models Cardiovascular Medicine

Recognizing Covid 19 Related Myocarditis The Possible Pathophysiology And Proposed Guideline For Diagnosis And Management Sciencedirect
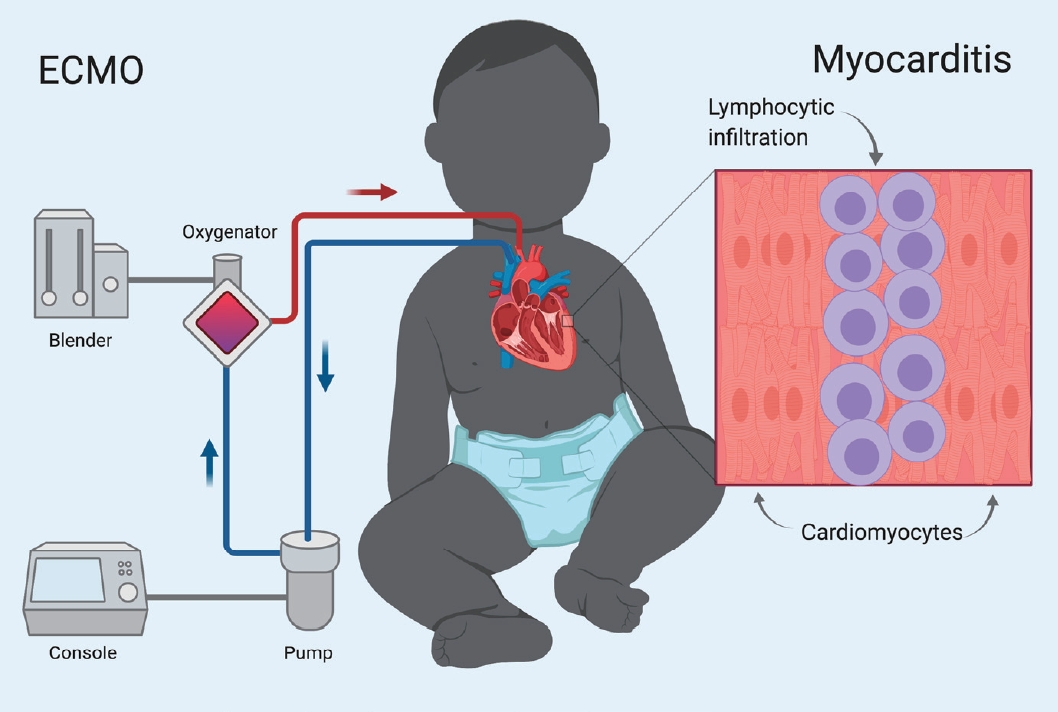
The Use Of Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation In Children With Acute Fulminant Myocarditis
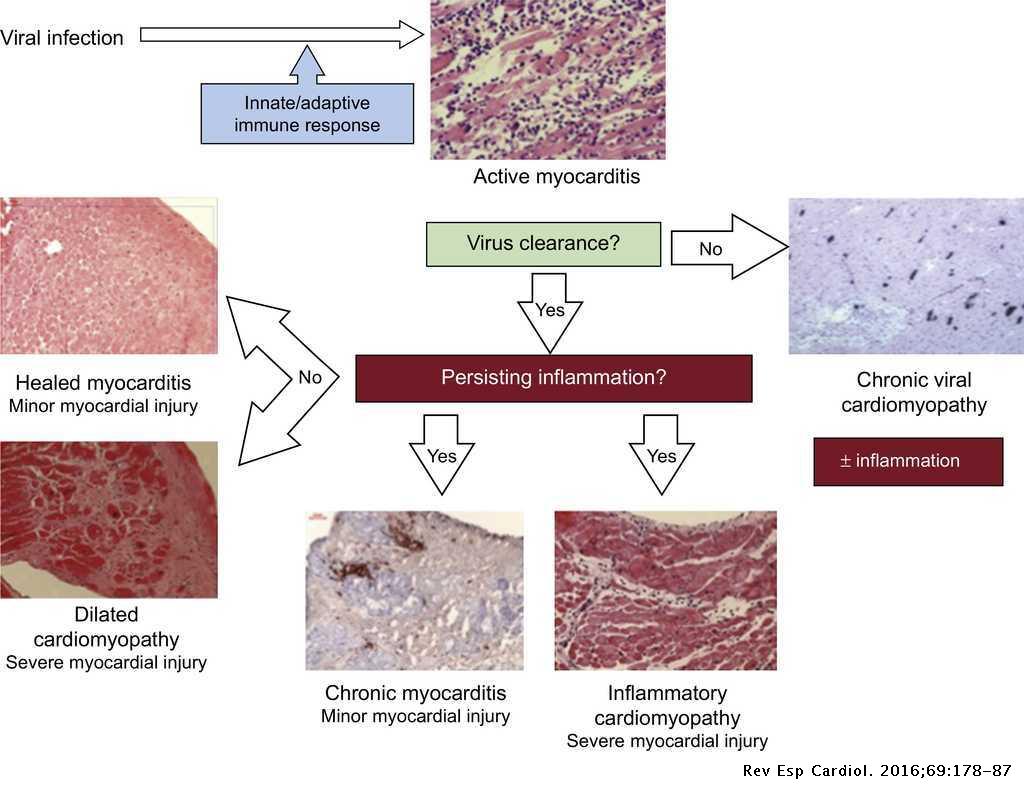
Update On Myocarditis And Inflammatory Cardiomyopathy Reemergence Of Endomyocardial Biopsy Revista Espanola De Cardiologia
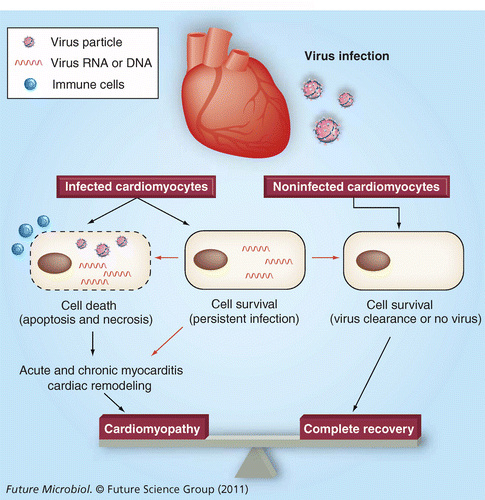
Viral Myocarditis Potential Defense Mechanisms Within The Cardiomyocyte Against Virus Infection Future Microbiology

Myocarditis In A Patient With Covid 19 A Cause Of Raised Troponin And Ecg Changes The Lancet

The Quest For New Approaches In Myocarditis And Inflammatory Cardiomyopathy Sciencedirect
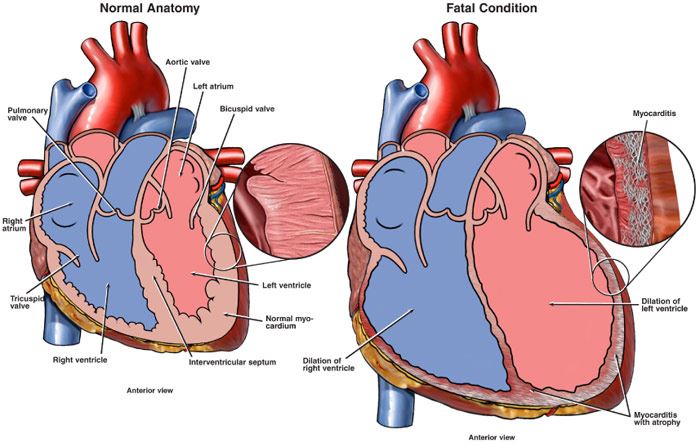
Myocarditis Diagnosis Symptoms And Treatment
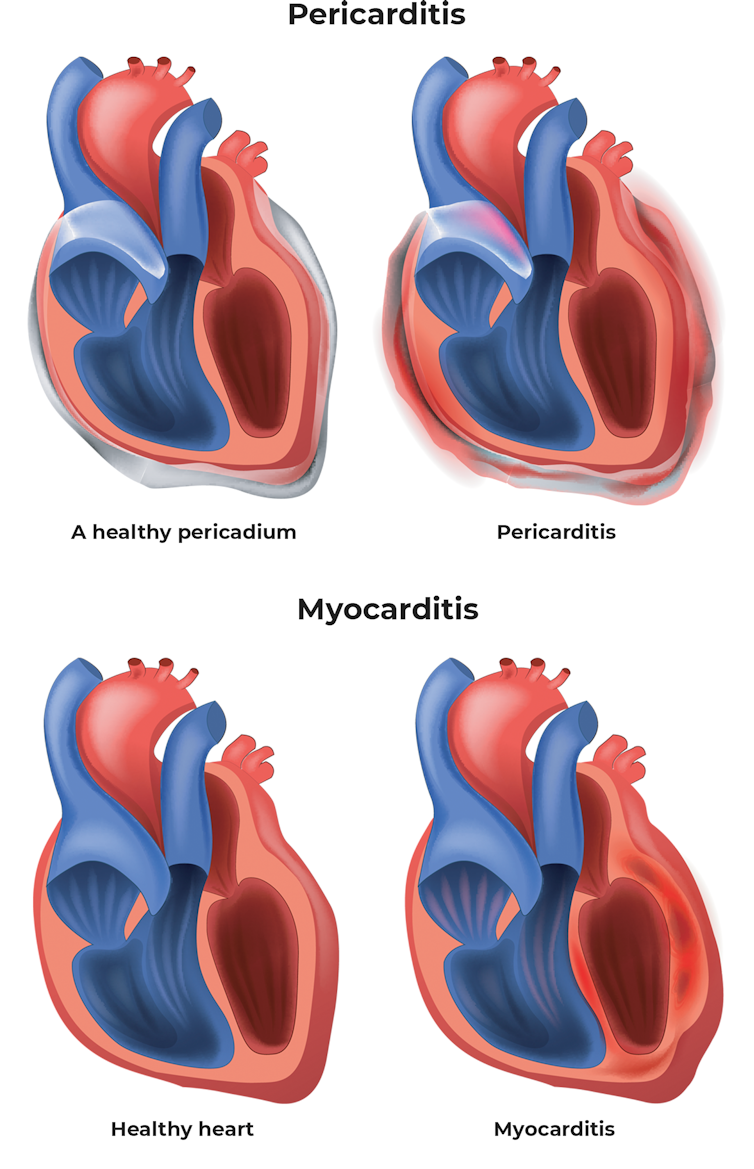
The Benefits Of A Covid Vaccine Far Outweigh The Small Risk Of Treatable Heart Inflammation
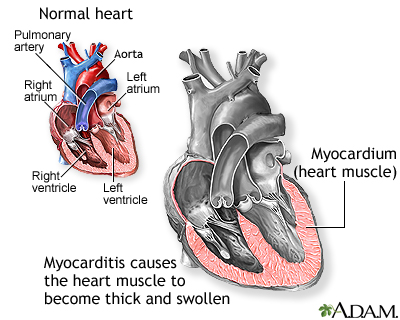
Myocarditis Medlineplus Medical Encyclopedia
Myocarditis Risk From Mrna Covid Vaccines Re Evaluated In Canadian Study Research Now Withdrawn